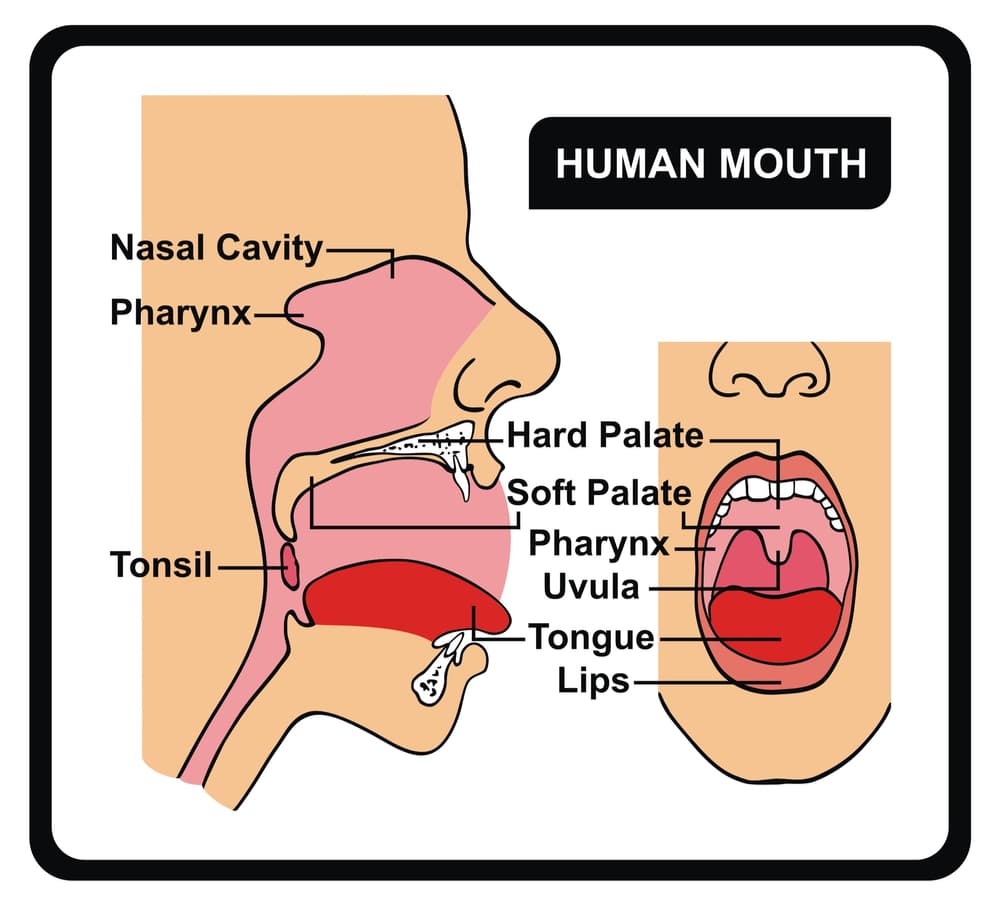
Human Mouth Anatomy
The oral cavity spans between the oral fissure (anteriorly - the opening between the lips), and the oropharyngeal isthmus (posteriorly - the opening of the oropharynx). It is divided into two parts by the upper and lower dental arches (formed by the teeth and their bony scaffolding).

Diagram of the Mouth 101 Diagrams
Mouth A molar tooth is located in the posterior (back) section of the mouth. It is found in most mammals that use their posterior teeth to grind food. Twelve molars are usually present in an.
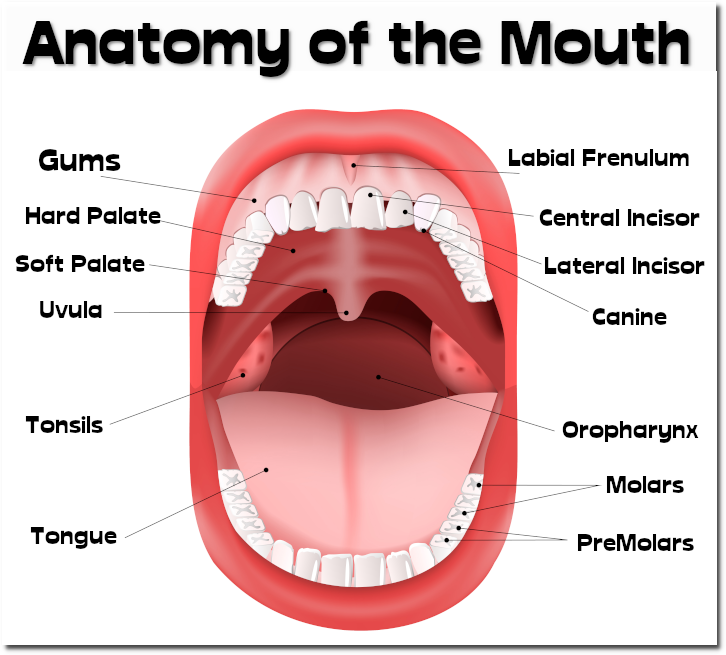
Anatomy of the Mouth
When we say 'mouth' we mean the oral cavity; a space in the lower part of the head that functions as the entrance to the digestive system. The content of the oral cavity determines its function. It houses the structures necessary for mastication and speech, which include the teeth, the tongue and associated structures such as the salivary glands.
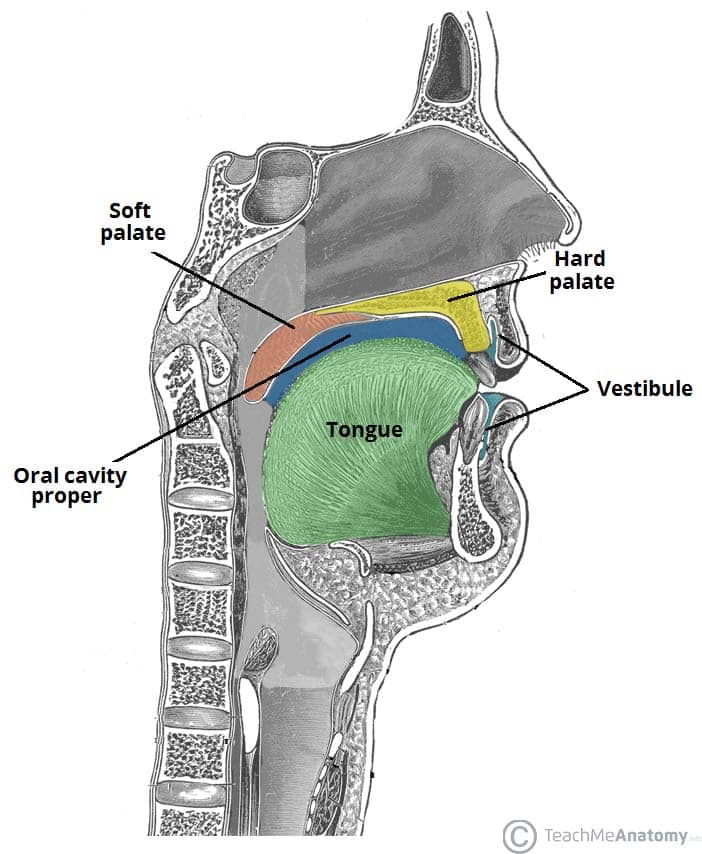
The Oral Cavity Divisions Innervation TeachMeAnatomy
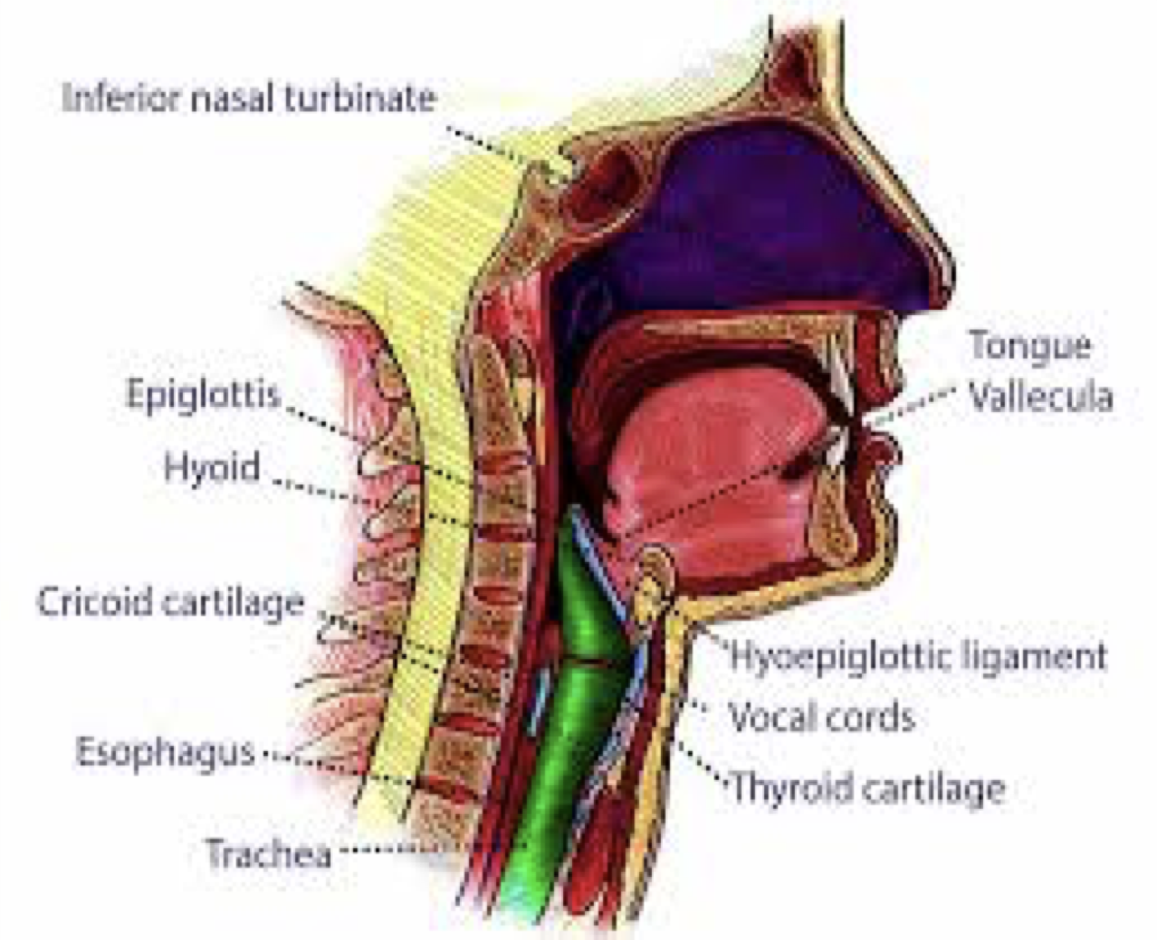
The pharynx (throat) is involved in both digestion and respiration. It receives food and air from the mouth, and air from the nasal cavities. When food enters the pharynx, involuntary muscle contractions close off the air passageways. Figure 6. The pharynx runs from the nostrils to the esophagus and the larynx.
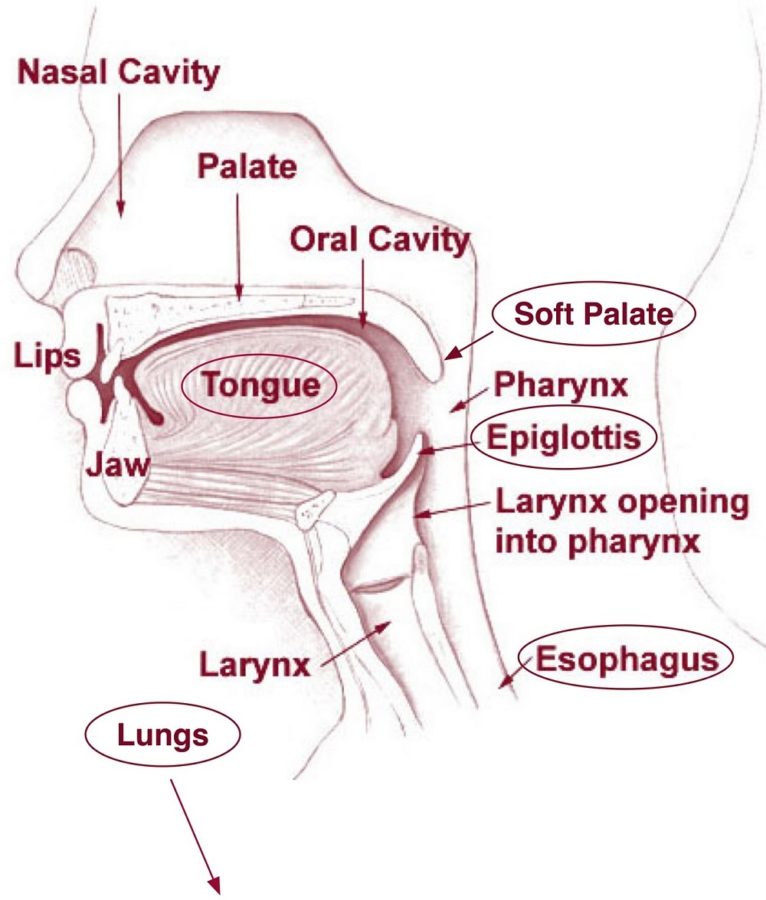
Diagrams of the Mouth 101 Diagrams
Mouth. The mouth, or oral cavity, is the first part of the digestive tract.It is adapted to receive food by ingestion, break it into small particles by mastication, and mix it with saliva.The lips, cheeks, and palate form the boundaries. The oral cavity contains the teeth and tongue and receives the secretions from the salivary glands.. Lips and Cheeks. The lips and cheeks help hold food in.

Oral cavity anatomy with educational labeled structure vector illustration
2D Interactive NEW 3D Rotate and Zoom + − Click To View Large Image Also known as the oral cavity, the mouth is the hollow cavity that allows food and air to enter the body. The mouth contains many other organs - such as the teeth, tongue, and the ducts of the salivary glands - that work together to aid in the ingestion and digestion of food.

Mouth Teeth Diagram with Label Health Images Reference
The mouth, also called the oral cavity, is the opening in the human skull that allows food, liquids, and air to enter the body. The oral cavity begins at the lips and ends at the throat. What are.
The Anatomy Of The Mouth
We have created 110 medical original illustrations of the mouth, the buccal cavity, the bones of the palate, the tongue, the salivary glands and the oral part of the pharynx with vessels and nerves.

The Mouth, Pharynx, and Esophagus Anatomy and Physiology II
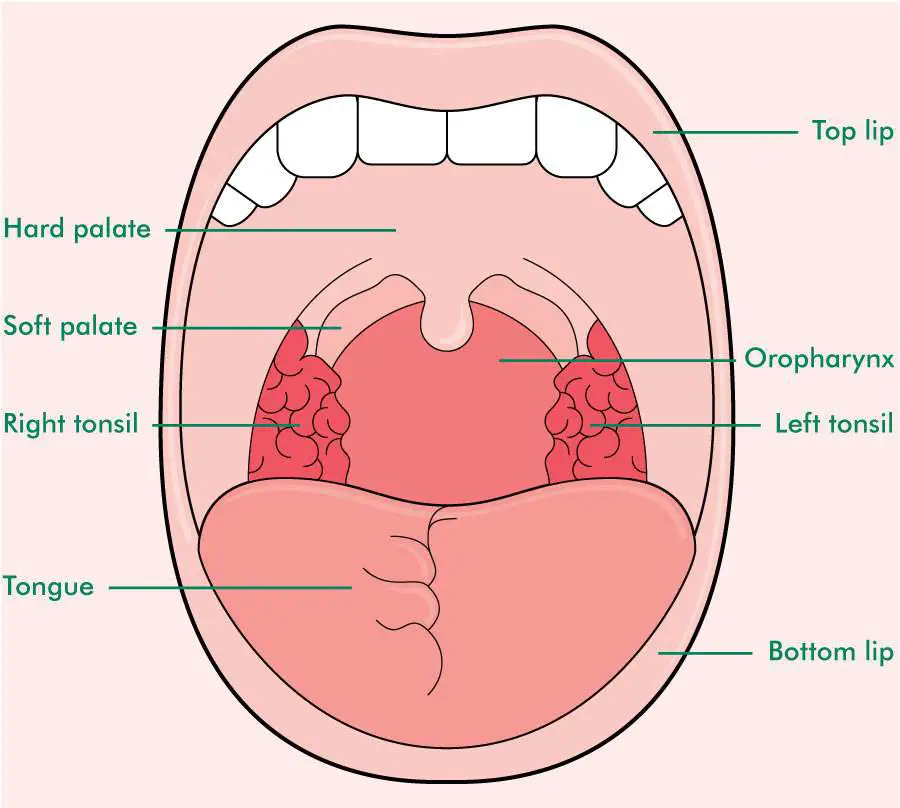
The boundaries of the oral cavity include the hard palate and soft palate that form the roof of your mouth, the tongue and the muscles below it, which make up the floor of the mouth and the inner surface of the lips in the front, the cheeks on the sides, and the uvula (the little "punching bag" shaped structure) at the end of your soft palate in.
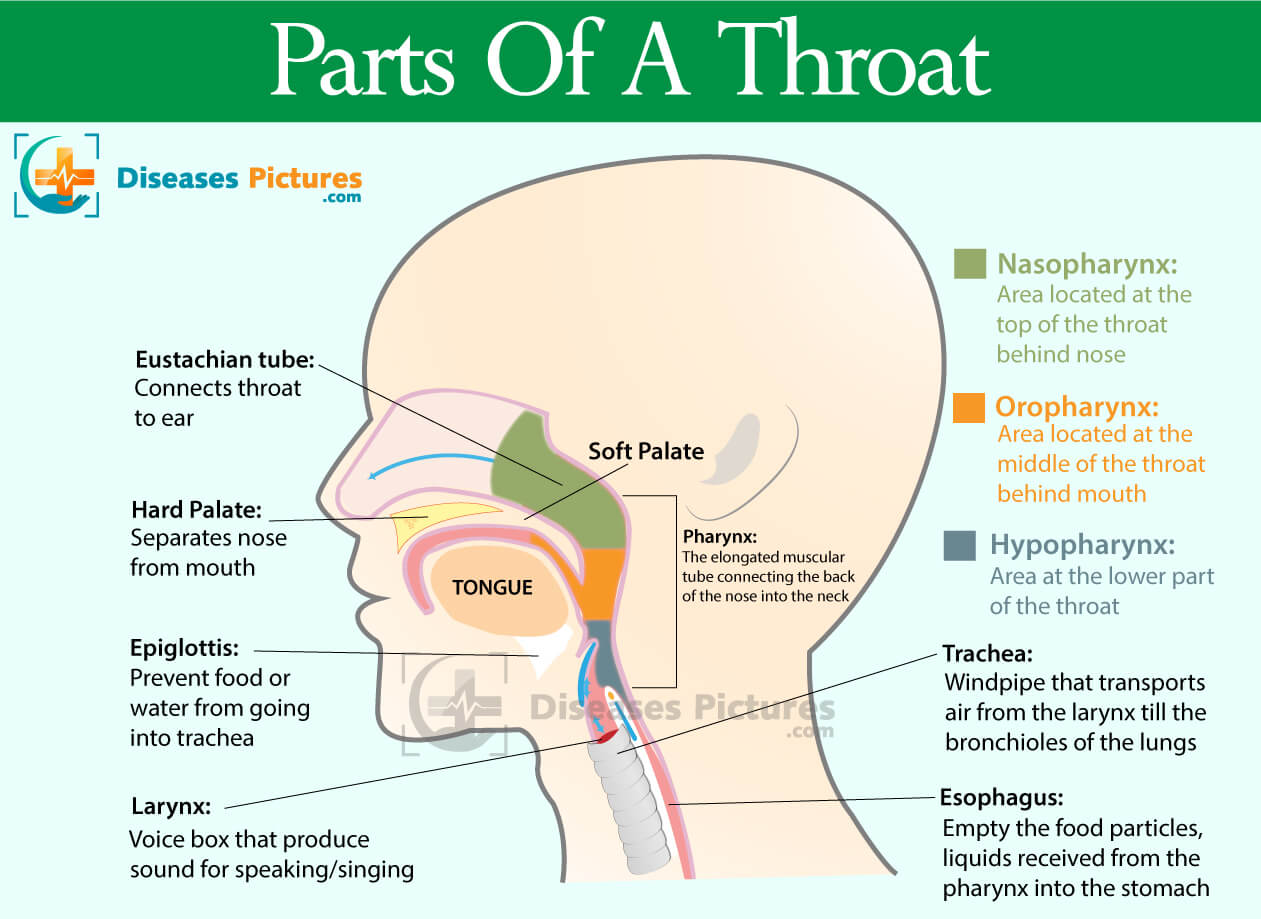
Throat Anatomy Throat Parts, Pictures, Functions HealthMD
The tongue is a mobile, muscular organ that lies within the mouth and partly extends into the upper throat. The tongue's anatomy is complex; it involves interlacing muscles, nerves, and a blood supply. This article will explain the details of tongue anatomy and how each part contributes to its movements and to functions such as eating, taste.
Mouth Diagrams Printable 101 Diagrams
The Human Body The oral cavity and vestibule are entirely lined by mucous membranes containing numerous small glands that, along with the three pairs of salivary glands, bathe the mouth in fluid, keeping it moist and clear of food and other debris.
Mouth diagram Healthiack
The mouth (oral cavity) consists of several components, including the teeth, gingiva (gums), tongue, palate, cheeks, lips and floor of the mouth. With the exception of the teeth, the mouth is lined by mucous membranes. The Teeth The teeth are held within the jaw bones and serve several important functions beyond allowing you to chew.

23.3 The Mouth, Pharynx, and Esophagus Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy. Under normal circumstances, the tongue is a pink, muscular organ located within the oral cavity proper. It is kept moist by the products of the major and minor salivary glands, which aids the organ as it facilitates deglutition, speech, and gustatory perception.While there is significant variability in the length of the tongue among individuals, on average, the organ is roughly 10 cm.

What is the Oral Cavity
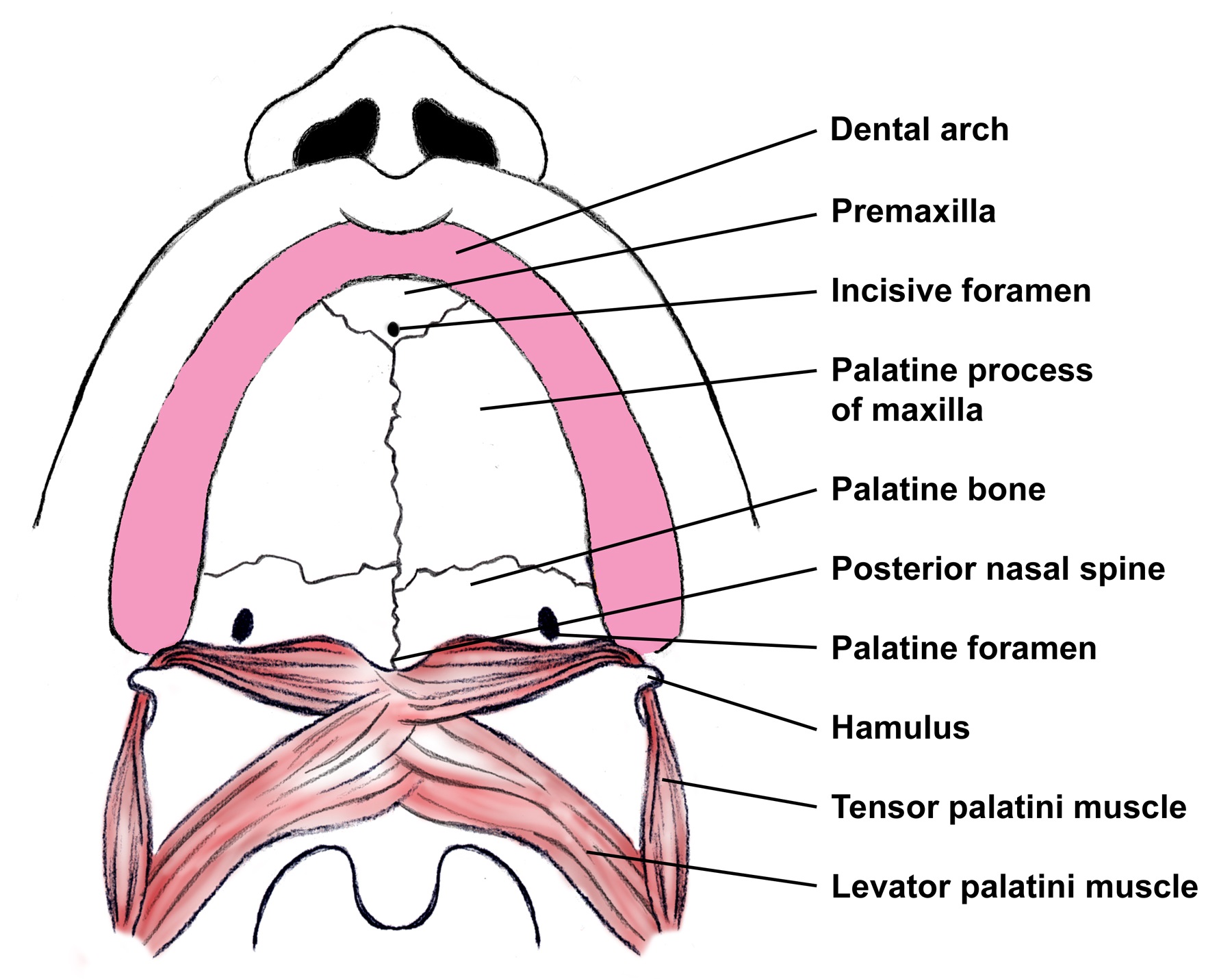
Anatomy of the Oral Cavity. Figure 1. Anterior view of the A external mouth and lips and B arterial supply to the lips. Figure 2. Inferior view of the maxilla. Figure 3. Cross section of a tooth. Figure 4. Lateral cross-section showing the A innervation of the lips B and teeth and gingiva.

Printable Mouth Diagrams 101 Diagrams
Lips Lips form the border of our mouth. Lips are a different color than the rest of our face because the skin around them is much thinner. Teeth and Gums The teeth are used to break up the foods that we eat. Teeth are made from enamel, the hardest substance found in our body.

Mouth Diagrams Printable 101 Diagrams
What is the mouth? Your mouth is an oval-shaped opening that sits just below your nose. It starts at your lips and ends towards your tonsils. Your mouth is part of your digestive system and respiratory system. Other names for your mouth include oral cavity. Advertisement Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.