
Instruction Decoder Schematic
The instruction decoder is the circuit that decodes an opcode. As an example, on the 6502 CPU, the opcode for the CLI (clear interrupt) instruction is 01011000 in binary. The CPU receives this as a set of digital logic signals on the data bus. How does it go from getting these signals to executing the procedure for the CLI instruction?

Is there a place where I can find 6502 instruction lines by opcode
The state machine within CPU is the instruction decoder.https://www.iklearn.com
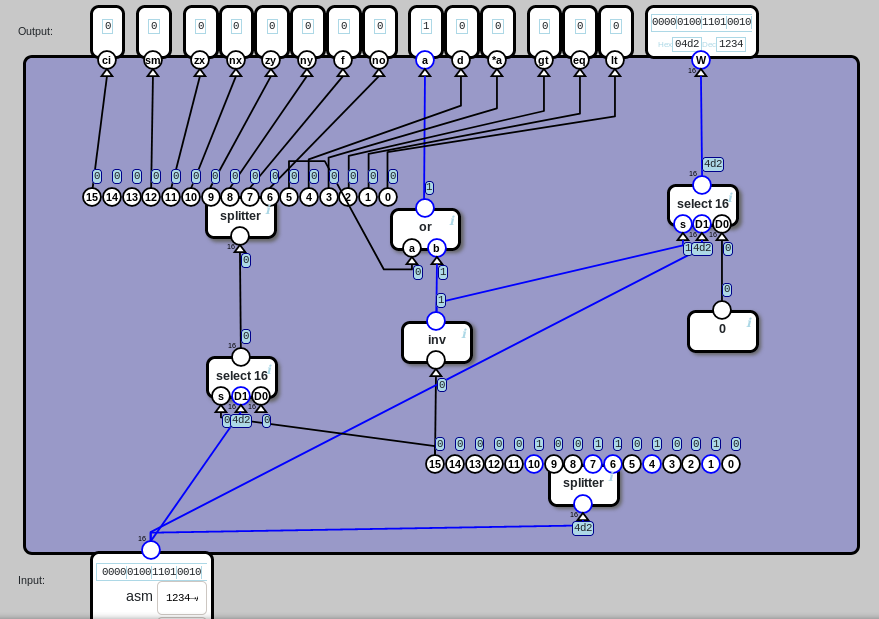
GitHub simsieg/nandgamesolutions Solutions for
The instruction decoder logic converts the op-code bits into settings for all the internal control lines. The operand provides a literal, file register address or program address, which will be used by the instruction.

Instruction Decoder. Download Scientific Diagram
Basic Principe of Decoder: As told earlier, the decoder is just a counter part of an Encoder. It takes a particular number of binary values as inputs and decodes then into more lines by using logic. A sample decoder is shown below which takes in 2 Lines as input and converts them to 4 Lines.

Decoder
A decoder is a circuit that converts an opcode into a signal or a set of signals that are used to control the circuitry of the microprocessor to enable it to perform the instruction defined by the opcode. A decoder may convert an opcode into an Enable input to control the circuitry. Shown below is an example of a simple decoder that decodes a 3.

CircuitVerse Instruction Decoder
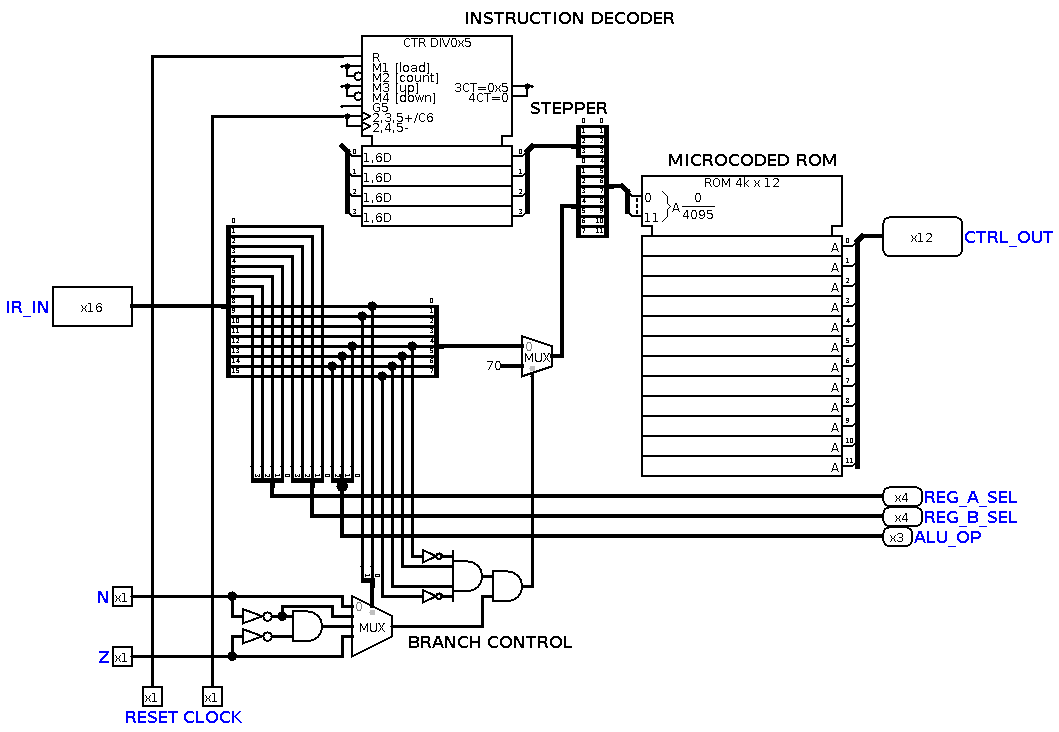
An instruction decoder takes in an instruction and outputs all of the control signals for that instruction. The other way to do it is to use ROM control. Every instruction implemented by a processor maps to an address in a Read-Only Memory (ROM) unit.. The main CPU circuit (located in cpu.circ) implements the main datapath and connects all.
A 16bit CPU in Logisim Hackaday.io
1. Exercise the complete CPU designed by last year's CS220 class. 2. Design the circuits for each of the pins on the Instruction Decoder. 3. Implement the Instruction Decoder. 4. Turn in the items described in Part 4. Part 1: Exercise the Complete CPU Drag the file MINIJVMFINAL.cct to the desktop, start up LogicWorks, and open this file.
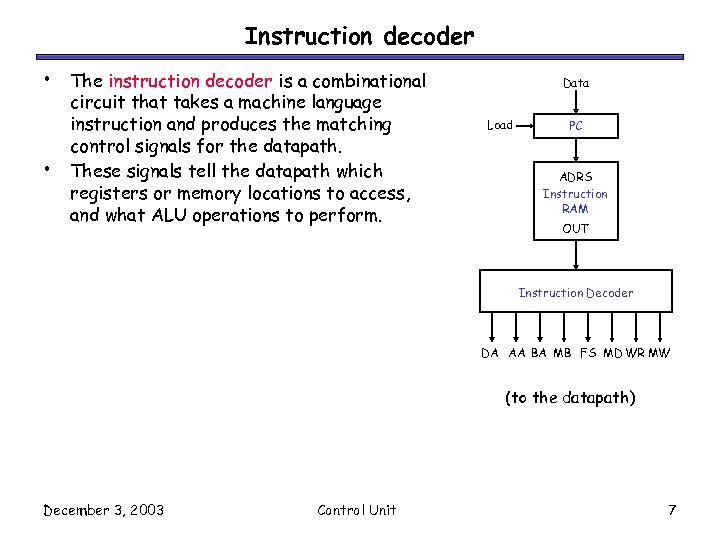
Control units In the last
The execution of an instruction in a standard digital computer occurs in three or four phases: Fetching the instruction from main memory or cache memory into the instruction register in the CPU. Decoding the instruction and generation of the data operand address (as in the case of a LOAD or a STORE instruction)

3.6 What Does This Have To Do With Computers, Anyway?
An Instruction Decoder is a circuit that processors implement in order to interpret instructions coming from memory. In synchronous designs, this circuit feeds the appropriate operands into the datapath of the processor, according to the instruction. Additionally, it must communicate with a Controller, whose role is to direct the flow of the.

Circuit Diagrams
The Instruction Decoder reads the next instruction in from memory, and sends the component pieces of that instruction to the necessary destinations. For each machine-language instruction, the control unit produces the sequence of pulses on each control signal line required to implement that instruction (and to fetch the next instruction).

2bit Decoder, 3bit Decoder, 4bit Decoder Computer Organization And
The instruction decoder takes an instruction like "SET R2 TO R1" and decodes it into something that the CPU can understand. It has its own internal register, called the "Instruction Register," which is where the current operation is stored. How exactly it does this comes down to the system you're running on, but once it's decoded, it will turn.

Decoder
Decoder •A decoder with i inputs and fully-populated outputs has 2 i outputs •It is generally better to work with both the input and output as buses rather than individual signals •Output is "one-hot" - One and only one output is high at a time •Common uses: - Selection of a word within a memory - Selection of one module

Integrated Circuit (16) Instruction Decoder YouTube
Instruction decoder: 4. Evaluate Operand Address Phase Compute address of the memory location of the instruction operand. Memory Circuitry: 5. Fetch Operands Phase Load MAR with address. Simple circuits, such as an adder, wired together, are part of the microcode.
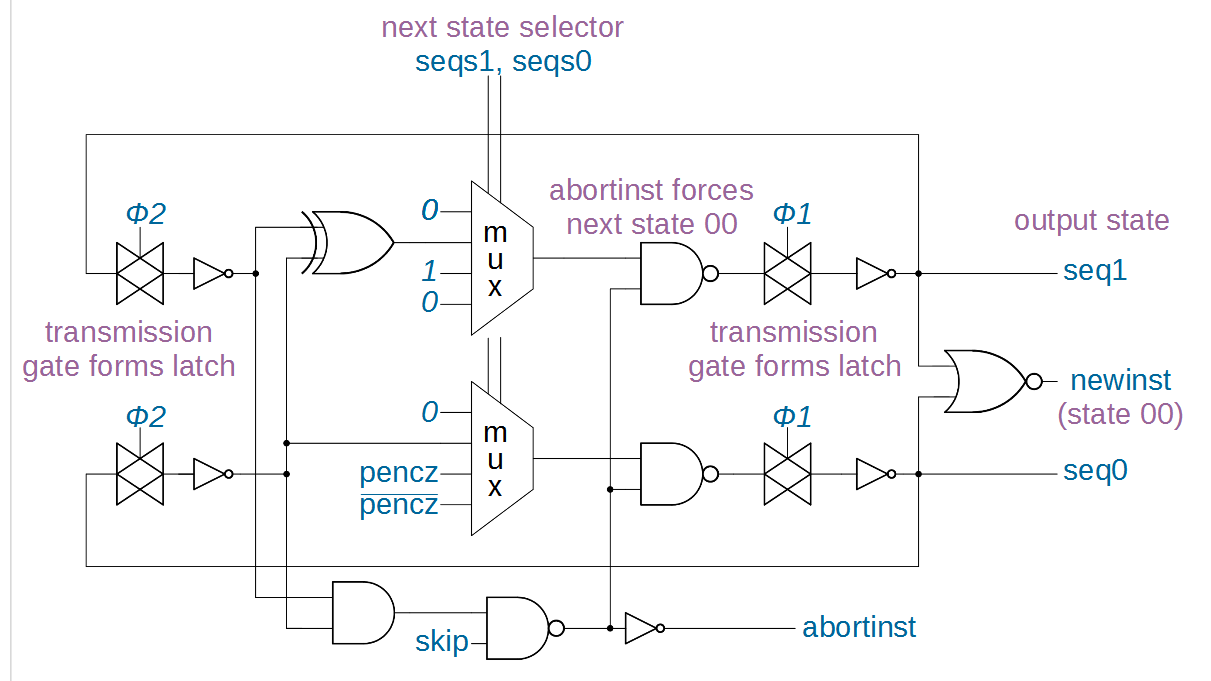
Reverse engineering ARM1 instruction sequencing, compared with the Z80
The instruction decoder of a processor is a combinatorial circuit sometimes in the form of a read-only memory, sometimes in the form of an ordinary combinatorial circuit. Its purpose is to translate an instruction code into the address in the micro memory where the micro code for the instruction starts.
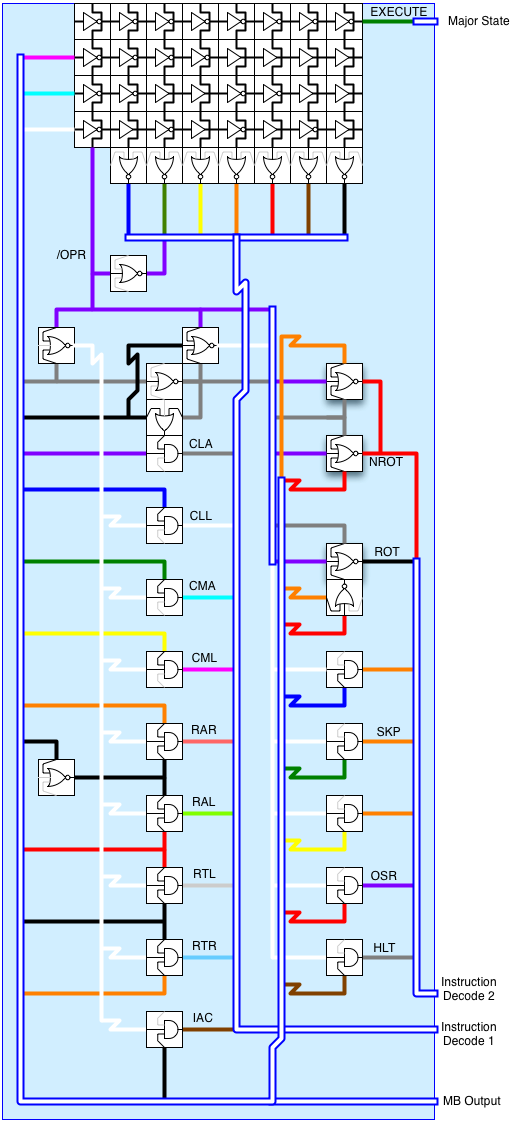
Instruction Decoder Layout
1. Encoders - An encoder is a combinational circuit that converts binary information in the form of a 2 N input lines into N output lines, which represent N bit code for the input. For simple encoders, it is assumed that only one input line is active at a time. As an example, let's consider Octal to Binary encoder.
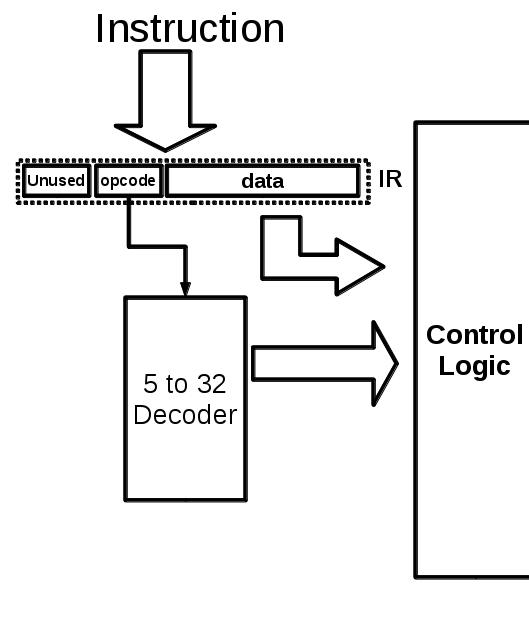
Instruction Decoder
Arm instructions are all 64-bits (8 bytes). So it is straightforward to load a block of memory and have eight decoders attack it, one starting at byte 0, a second at byte 8, up to the eighth starting at byte 56. But x86 is a CISC architecture, and so the instructions vary in length from 1 to 15 bytes.